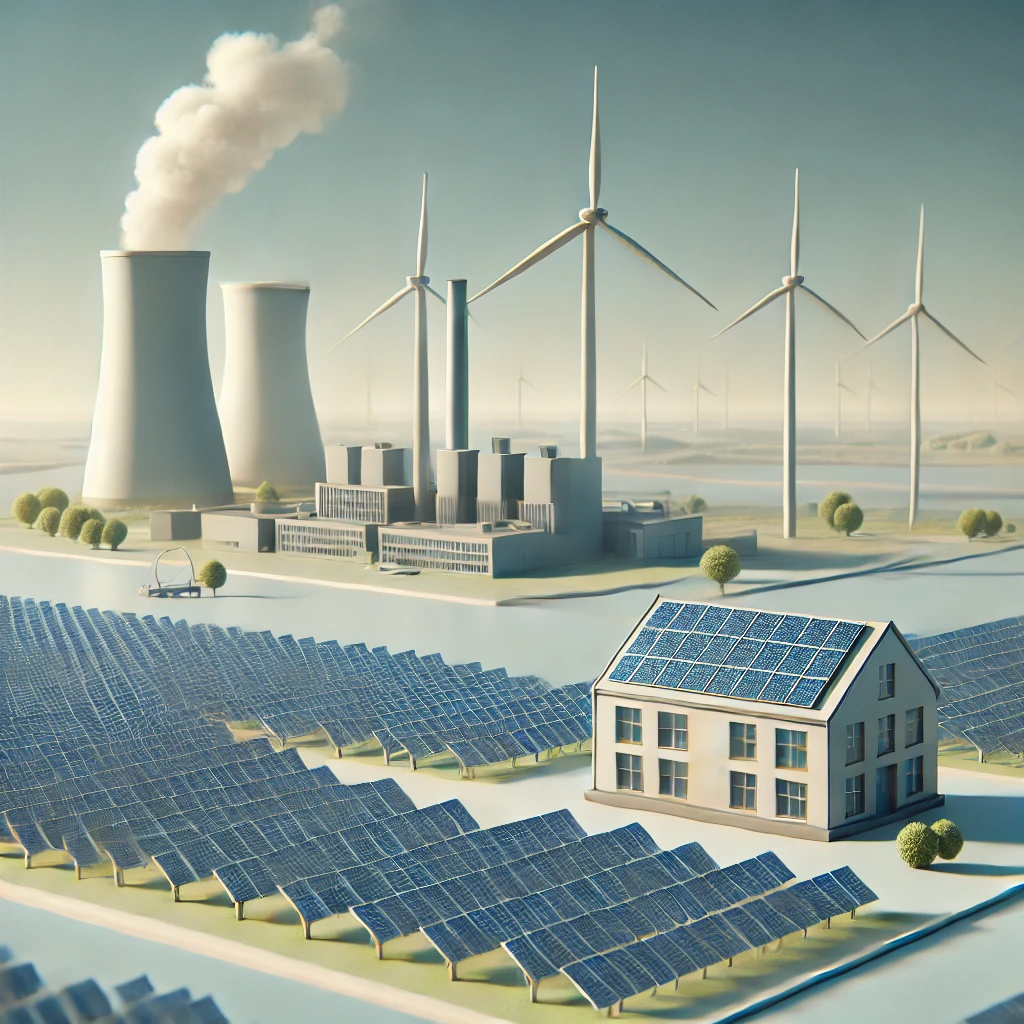
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing humanity today, with rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, and extreme weather patterns becoming more common. A major driver of climate change is the excessive release of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, primarily from the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. These emissions have led to a steady increase in global temperatures, triggering a series of environmental and socio-economic challenges.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal, offer a powerful solution to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change. By replacing fossil fuels with clean, sustainable energy, we can significantly decrease the amount of greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere, while also creating a more resilient and sustainable energy system for the future.
Why Renewable Energy is Key to Combating Climate Change
1. Eliminating Carbon Emissions
The primary benefit of renewable energy is that it generates electricity without producing carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. Unlike fossil fuels, which release vast amounts of CO₂ when burned, renewable energy sources harness natural processes that are inherently low-emission or emission-free. For example:
- Solar power captures energy from the sun using photovoltaic cells, producing electricity with zero emissions.
- Wind power generates electricity through wind turbines, harnessing natural wind currents with no direct emissions.
- Hydropower uses the energy of flowing water to turn turbines and produce electricity without burning fuels.
- Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate power, typically releasing only trace amounts of emissions.
These technologies are crucial in reducing the global carbon footprint. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), switching to renewables could cut global CO₂ emissions by nearly 70% by 2050.
2. Reducing Dependency on Fossil Fuels
The global energy system is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels, which account for over 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This dependency makes it difficult to achieve meaningful reductions in emissions. However, by transitioning to renewable energy, we can drastically reduce our reliance on coal, oil, and natural gas. This transition is critical for long-term climate stability.
Countries like Germany, Denmark, and Costa Rica have made significant strides in reducing fossil fuel use by integrating more renewables into their energy grids. As more nations follow suit, the demand for fossil fuels will decrease, helping to reduce global carbon emissions on a larger scale.
3. Creating a Sustainable Energy Future
Renewable energy is not only clean but also sustainable. Fossil fuels are finite resources, and as reserves dwindle, the cost of extracting and burning them will increase. In contrast, renewable sources like sunlight, wind, and water are virtually limitless. By investing in renewable infrastructure, countries can ensure a stable, long-term supply of energy while reducing their environmental impact.
Furthermore, renewable energy reduces the risk of environmental disasters associated with fossil fuel extraction, such as oil spills, coal mining accidents, and natural gas leaks, all of which contribute to environmental degradation and climate change.
Types of Renewable Energy and Their Role in Emission Reduction
1. Solar Energy
Solar energy is one of the most abundant and accessible renewable resources on Earth. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, providing a clean and reliable energy source. The technology behind solar energy has become increasingly efficient and affordable, making it a viable option for both individual households and large-scale power plants.
- Impact on Emission Reduction: Solar energy has the potential to eliminate millions of tons of CO₂ emissions annually. For example, a single residential solar system can reduce an average home’s carbon footprint by over 3,000 pounds per year. On a larger scale, solar farms contribute significantly to reducing reliance on coal and gas-powered electricity generation.
2. Wind Energy
Wind energy harnesses the power of wind through turbines that generate electricity. Wind farms can be located on land (onshore) or in the ocean (offshore). Wind power is particularly effective in regions with strong and consistent wind patterns, such as coastal areas and open plains.
- Impact on Emission Reduction: Wind energy is a critical part of the renewable energy mix. According to the Global Wind Energy Council, wind energy avoided over 1 billion tons of CO₂ emissions in 2020 alone. As wind power expands, especially offshore wind projects, it has the potential to displace a large portion of fossil fuel-based energy.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower is one of the oldest forms of renewable energy, using the movement of water to generate electricity. Hydropower plants can be small (serving individual communities) or large-scale, such as dams that produce electricity for entire regions. While it is a clean energy source, hydropower projects need to be carefully managed to avoid disrupting ecosystems and water supply.
- Impact on Emission Reduction: Hydropower already accounts for a significant portion of global renewable energy, providing about 16% of the world’s electricity. By expanding the use of hydropower, particularly through small-scale and run-of-the-river systems, we can further reduce emissions without causing environmental harm.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat to produce electricity or provide direct heating. It is a reliable and consistent energy source, as the Earth’s heat is available 24/7, unlike solar and wind, which are dependent on weather conditions.
- Impact on Emission Reduction: Geothermal plants emit very low levels of CO₂, and in some cases, they are virtually emission-free. Geothermal energy is particularly important for reducing emissions in areas with high geothermal activity, such as Iceland, where geothermal power accounts for nearly all of the country’s electricity and heating.
The Challenges of Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Despite the clear benefits, the transition to renewable energy is not without its challenges. Some of the key obstacles include:
1. Intermittency and Storage
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent, meaning they don’t always produce power when demand is highest (e.g., during cloudy or windless days). This intermittency issue highlights the need for improved energy storage solutions, such as advanced batteries or pumped hydro storage, to store excess power and release it when needed.
2. Infrastructure and Grid Integration
Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy requires significant investments in infrastructure, including upgrading electrical grids to handle the variability of renewable power. Many current grids are not designed to accommodate high levels of renewable energy, leading to inefficiencies and power disruptions.
3. Initial Costs
The upfront cost of renewable energy technologies can be a barrier, especially for developing countries. While renewable energy has become more cost-competitive, initial investments in solar farms, wind turbines, or geothermal plants can be substantial. However, the long-term savings from reduced fuel costs and lower emissions often outweigh these initial expenses.
4. Political and Social Resistance
In some regions, political and social resistance to renewable energy adoption can slow progress. This resistance may come from vested interests in the fossil fuel industry, concerns about job losses in traditional energy sectors, or skepticism about the reliability of renewables.
The Path Forward
Renewable energy is essential for reducing global carbon emissions and combating climate change. By transitioning away from fossil fuels and investing in clean, sustainable energy sources, we can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions, create a more resilient energy system, and ensure a healthier planet for future generations.
To achieve these goals, governments, industries, and individuals must work together to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy. This includes implementing supportive policies, investing in research and development for better storage technologies, and modernizing infrastructure to integrate more renewable energy into the grid.
The path toward a renewable future is clear. By acting now, we can harness the power of the sun, wind, water, and Earth to reduce emissions, combat climate change, and build a sustainable world.